Gamifying Number Recognition: A Mobile Learning Approach for Primary Students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/cjiep.1.1.113Keywords:
Mobile learning, early numeracy development, gamified learning, mathematics educationAbstract
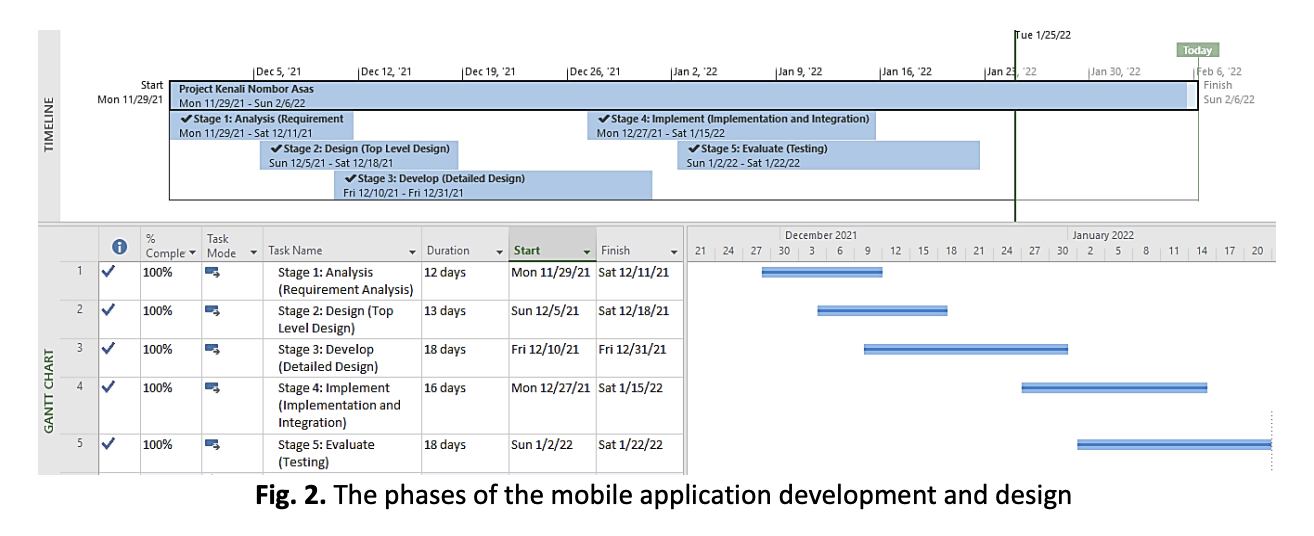
The rapid evolution of educational technology has led to the increased adoption of mobile learning (M-learning) as a tool to enhance teaching and learning. This study investigates the development and evaluation of "Kenali Nombor Asas", a mobile learning application designed to assist young learners, particularly primary school students, in recognizing and understanding basic numbers (0–9). Despite the growing integration of digital learning tools, students continue to face difficulties in numeracy acquisition, which can hinder their overall mathematical competency. The study aims to address this gap by developing an interactive mobile application that incorporates behavioral learning principles to reinforce number recognition skills through structured exercises and gamified learning experiences. The research employs the ADDIE instructional design model, ensuring a systematic approach to app development, from analysis and design to implementation and evaluation. Data were collected from a small cohort of primary school students using a questionnaire-based perception survey featuring a smileyometer scale and interviews with teachers. Findings indicate that students responded positively to the application, with all participants stating that the app was engaging, easy to use, and beneficial in learning mathematics. The analysis of student and teacher feedback revealed three key themes that reflect both the strengths and areas for improvement of the application: (i) increased engagement and motivation, (ii) ease of use and accessibility, and (iii) need for navigation and content enhancements. However, areas for improvement were identified, particularly in navigation and content accessibility. Based on these insights, recommendations include refining the app’s user interface, incorporating adaptive learning features, and expanding its application to a broader demographic. In conclusion, this study demonstrates the potential of mobile learning applications in supporting early mathematics education, emphasizing the need for further research involving larger sample sizes and more rigorous performance assessments to validate its effectiveness.